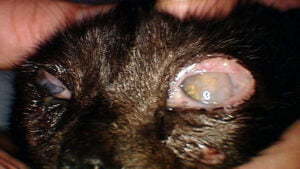
Herpesvirus and chlamydial eye infections in cats
Feline herpesvirus-1 (FHV-1) and chlamydia are the most common infectious organisms that cause conjunctivitis and corneal ulcers in kittens, and less frequently in adult cats.
Infection with these pathogens is very common, especially in cats in shelters and in households with multiple cats. Clinical signs include fever, sneezing, coughing, salivation, excessive tearing, swelling, and redness of the conjunctiva. These pathogens spread from cat to cat by direct contact or air (via aerosol).
Cats infected with FHV-1 become carriers of the virus for life, and the virus can become active and cause re-infection in conditions when the cat’s immune system weakens (due to stress or the use of systemic immunosuppressive drugs). FHV-1 infection is usually treated with antiviral drops and/or systemic antiviral drugs. Chlamydia infection can be successfully controlled by long-term use of an appropriate systemic antibiotic.